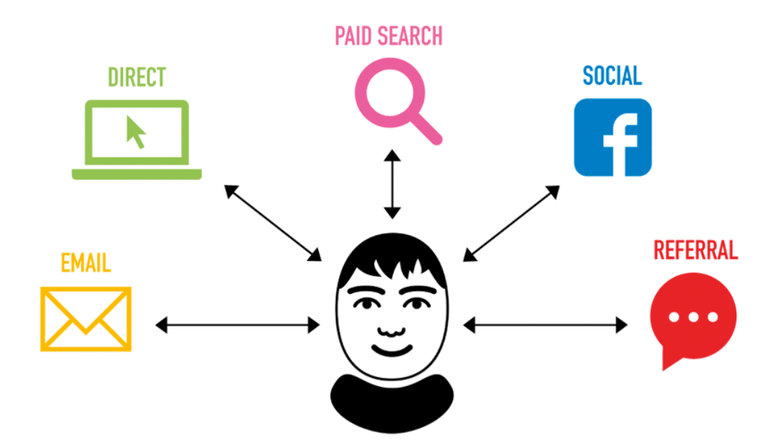
We take a look at the two data driven attribution models used in marketing.
- Shapley value
- Markov Model
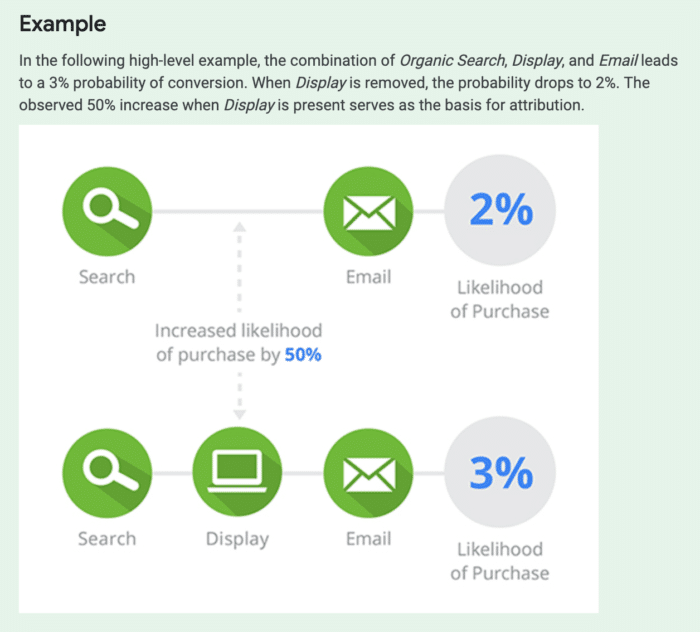
Illustration of the Shapley Value by Google:
source: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/3191594?hl=en
What is a Markov model?
For attribution modelling purposes, a Markov model is a way to chart out the customer interaction cycle. You specify individual states in that process as vertices in a chain. You calculate the probability of transition from one particular state in the chain to a different state in a chain (for example, the probability of a visit to a Twitter page to lead to a click to the company’s main website, as well as the probability of that Twitter page visit being the last interaction (leading to a failed conversion attempt).
Let’s go back to our friend Brand X. They peek at the data from their customer interaction history. Let’s say that they have five marketing channels as defined below:
- ChSEO: a search-engine-optimized website, to allow for high ranking in organic search results.
- ChYT: YouTube videos, including ones embedded in the website.
- ChTW: an active Twitter account.
- ChDIS: display ads on other websites via a Google-based ad channel.
- ChTV: television advertising.
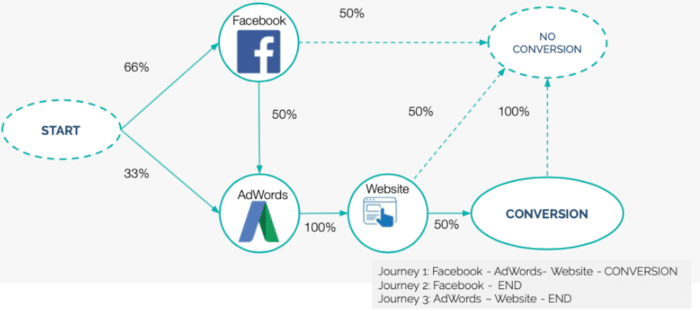
You see that there are, say, five different customer “journeys”:
- ChTV -> no conversion
- ChTV -> ChSEO -> conversion
- ChSEO -> ChYT -> ChDIS -> conversion (as in the example given above)
- ChTW -> ChDIS -> ChSEO -> conversion
- ChSEO -> ChYT -> no conversion
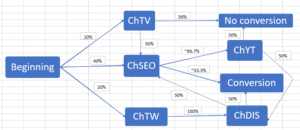
From here, we can calculate the probabilities of customers finding themselves at different parts of the customer journey, and transitioning from those states to another state in the Markov chain. Here’s our chart showcasing that:
| Vertix | Transition | Chance | Total Chance |
| Beginning | ChTV | 20% | 40% |
| Beginning | ChTV | 20% | |
| Beginning | ChSEO | 20% | 40% |
| Beginning | ChSEO | 20% | |
| Beginning | ChTW | 20% | 20% |
| ChTV | No conversion | 50% | 50% |
| ChTV | ChSEO | 50% | 50% |
| ChSEO | ChYT | ~33.3% | ~66.7% |
| ChSEO | ChYT | ~33.3% | |
| ChSEO | Conversion | ~33.3% | ~33.3% |
| ChYT | No conversion | 50% | 50% |
| ChYT | ChDIS | 50% | 50% |
| ChDIS | ChSEO | 50% | 50% |
| ChDIS | Conversion | 50% | 50% |
| ChTW | ChDIS | 100% | 100% |
Success! We have a straightforward, mathematical breakdown of the chances of a consumer transitioning from one state to another. We know:
- Which channel consumers will start at;
- Which ones they will transition to; and
- Which channels will consumers be in directly preceding a non-conversion or a conversion.
Now let’s plan it out in a Markov chain:
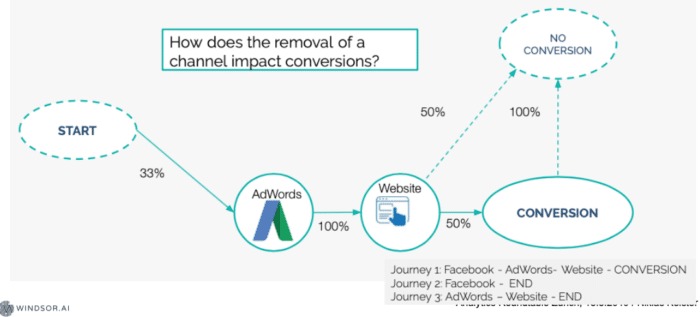
How does this demonstrate the superiority of Markov models?
Let’s go through the same customer journey we looked at earlier:
ChSEO -> ChYT -> ChDIS -> conversion
In a last click model, we attribute the Google Display Ads with 100% of the credit for the conversion. However, in the Markov model we see the real value that the search-engine-optimized website has for driving conversion; we see the value it has in driving traffic to the banner ads, as well as its leading role in a number of successful consumer journeys.
Markov Model:
The removal effect of the Markov attribution model:
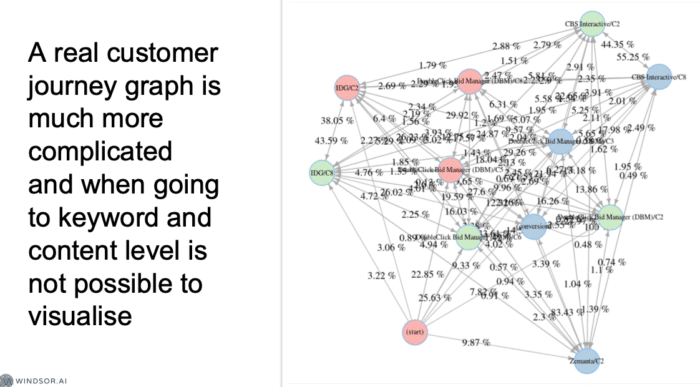
A real markov model with customer journeys:
Summary
Here at Windsor.ai, we drill deep into data, ensuring that the best insights can be extracted from the information available to you. Our experience has led us to believe that Markov models are the best option from those available for attribution modelling. A Markov model is a probabilistic model, which focuses on specific calculations of the chance that an interaction in one channel will transition to a different state, such as a conversion.
Windsor.AI’s Attribution Insights solution generates easy-to-read Markov models to gain real insight into how your marketing efforts are performing.

Try Windsor.ai today
Access all your data from your favorite sources in one place.
Get started for free with a 30 - day trial.